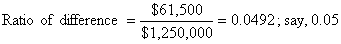| 350 | ECONOMICS OF BRIDGEWORK | Chapter XXXIII |
| Schedule B. | |
| Earthwork | $0.50 X 1.25 = $0.625 |
| Loose rock | 1.00 X 1.25 = 1.25 |
| Solid rock | 1.50 X 1.25 = 1.875 |
| Concrete | 20.00 X 1.25 = 25.00 |
| Wooden trestle | 50.00 X 1.25 = 62.50 |
| Steelwork | 0.08 X 1.25 = 0.10 |
|
The actual quantities of the materials in the completed job were, as follows: |
| Earthwork | 980,000 cu. yds. |
| Loose rock | 110,000 " |
| Solid rock | 50,000 " |
| Concrete | 10,500 " |
| Wooden trestle | 2,100 lin. ft. |
| Steelwork | 480,000 lbs. |
|
In addition, there was done by the contractor certain "unclassified work" which actually cost him for labor and materials $20,000. The revised estimate is, therefore, as follows: |
| Earthwork | 980,000 cu. yds. @ $0.625 = $612,500 |
| Loose rock | 110,000 " @ 1.25 = 137,500 |
| Solid rock | 50,000 " @ 1.875 = 93,750 |
| Concrete | 10,500 " @ 25.00 = 262,500 |
| Wooden trestle: | 2,100 lin. ft. @ 62.50 = 131,250 |
| Steelwork | 480,000 lbs. @ 0. 10 = 48,000 |
| Unclassified work | $20,000 X 1.3 = 26,000 |
| Summation, or "Sum D" | = $1,311,500 |
|
The difference between "Sum D" and "Sum C" equals $1,311,500- $1,250,000 = $61,500.
For this ratio, the diagram, Fig. 33b, gives a corrective ratio of 0.865, which multiplied by $61,500 gives $53,198, say, $53,200, making the corrected limit, or "Sum E," = $1,250,000 + $53,200 = $1,303,200. If the total actual cost of the work, including that of the unclassified work without allowance for superintendence or overhead, amounted to $1,100,000, the total profit would be: $1,303,200 - $1,100,000 = $203,200. Of this, the joint share of the contractor and the owner would be: $203,200 ÷ 1.25 = $162,560; |